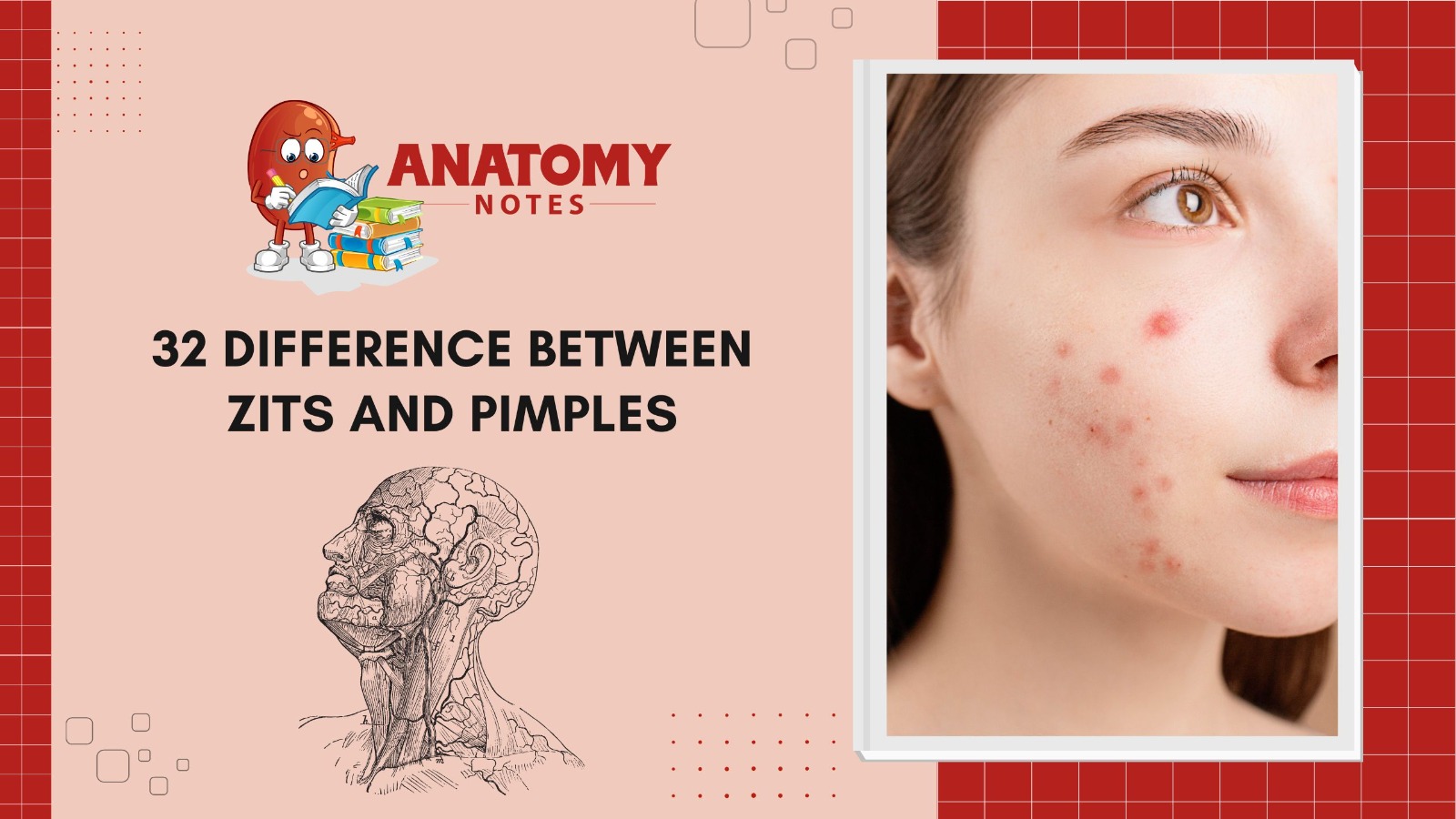
People sometimes use “zits” and “pimples” interchangeably, however, they are two separate forms of acne patches with subtle differences in appearance and etiology. Knowing these distinctions might help you pick skin care and healing approaches. People call “zits” or “whiteheads,” closed comedones. They occur when skin oil and dead cells clog hair shafts. This raises a tiny lump on the skin. Zits have a white or yellowish head of pus and dead skin cells under the skin. These areas are usually not heated or inflamed and are considered less dangerous than other acne forms.
Conversely, pimples are acne lesions such as papules, pustules, and nodules. Zits are smaller and less noticeable than pimples. Small, red, raised bumps with no core are called pustules, whereas pustules have a white or yellowish pus-filled center. Deep under the skin, nodules are larger, thicker, and occasionally painful pimples.
Zits and pimples differ mostly in appearance and pain. Zits are smaller and less red than pimples. They may have clear white or yellow heads. Acne pimples are more noticeable. The head may be cloudy and they are generally red and swollen. Most pimples are caused by hair follicle bacteria, mainly Propionibacterium acnes. Zits and pimples can be avoided and treated with mild washing, exfoliation, and cosmetic treatments like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids. Oral antibiotics, prescription skin medications, or isotretinoin may be needed for severe acne.
Even though “zits” and “pimples” are sometimes used interchangeably, they are two forms of acne lesions with differing inflammation and appearance. Zits are less red than pimples and feature little white or yellowish heads. However, pimples are more diverse, red, bloated, and different-looking. Understanding these variations helps people choose acne-friendly skin care and treatment regimes.
Also Read: Human Skin: Definition, Layers, Types, & Diseases
Here are the 32 differences between zits and pimples:
|
S.No. |
Aspect |
Zits |
Pimples |
|
1 |
Terminology |
Informal term for acne pimples |
Formal term for acne lesions |
|
2 |
Medical Term |
May not be used in a medical context |
Medical term commonly used by dermatologists |
|
3 |
Appearance |
Small, red, inflamed bumps on the skin |
Small, red or white bumps on the skin |
|
4 |
Size |
Can vary in size, from tiny to larger |
Typically small, not usually very large |
|
5 |
Causes |
Typically caused by clogged pores and excess oil |
Result from clogged hair follicles and excess oil production |
|
6 |
Severity |
Can range from mild to moderate |
Can vary in severity from mild to severe |
|
7 |
Location |
Can occur anywhere on the body, including the face |
Commonly appear on the face, chest, and back |
|
8 |
Pain |
May or may not be painful |
Can be painful, especially when touched |
|
9 |
Duration |
Can be short-lived or persistent |
May last for a few days to several weeks |
|
10 |
Whitehead vs. Blackhead |
Can develop into whiteheads or blackheads |
May evolve into whiteheads or remain red and inflamed |
|
11 |
Appearance of Pus |
May contain pus at the center |
Can have a white or yellow pus-filled center |
|
12 |
Inflammation |
Can be inflamed or non-inflamed |
Often inflamed, causing redness and swelling |
|
13 |
Itching |
May or may not be accompanied by itching |
Itching is a common symptom |
|
14 |
Comedones |
Can be non-comedonal or comedonal |
Typically comedonal, non-comedonal less common |
|
15 |
Severity of Scarring |
Less likely to leave permanent scars |
Can lead to scarring, especially if picked or squeezed |
|
16 |
Elevation |
Can be raised or slightly elevated |
Often raised, with a noticeable bump |
|
17 |
Types |
May include pustules, papules, or nodules |
Primarily papules and pustules |
|
18 |
Underlying Factors |
Can be influenced by hormonal changes, genetics, and skincare habits |
Hormonal changes, genetics, and hygiene practices can play a role |
|
19 |
Treatment |
Over-the-counter creams, good hygiene practices, and medical interventions if severe |
Over-the-counter treatments and prescription medications, such as antibiotics or retinoids |
|
20 |
Pore Blockage |
Often results from blocked oil glands |
Usually caused by the clogging of hair follicles |
|
21 |
Squeezing Risk |
Squeezing may lead to infection and scarring |
Squeezing can worsen inflammation and increase the risk of scarring |
|
22 |
Occurrence Frequency |
May occur sporadically or frequently |
Can occur frequently, especially during adolescence |
|
23 |
Bacterial Involvement |
Bacterial infection may be present but not always |
Bacterial infection is often involved |
|
24 |
Follicle Involvement |
Typically less related to hair follicles |
Usually associated with hair follicles |
|
25 |
Age Group |
Can affect individuals of all ages |
More common during adolescence |
|
26 |
Prevention |
Good skincare practices and avoiding touching the face can help prevent zits |
Practicing good hygiene and avoiding squeezing can help prevent pimples |
|
27 |
Oil Production |
May involve excess oil production |
Often linked to increased sebum production |
|
28 |
Medical Evaluation |
May not always require a doctor’s evaluation |
Severe cases or persistent pimples may require medical assessment |
|
29 |
Appearance of Zits |
May appear as red or pink bumps |
Can be red, pink, or have a white or yellow center |
|
30 |
Hormonal Influence |
Hormones can play a role in zit development |
Hormonal fluctuations can trigger pimples |
|
31 |
Infection Risk |
Infection risk may be lower |
Higher risk of infection, especially if not treated properly |
|
32 |
Emotional Impact |
Impact on self-esteem and confidence can vary |
May affect self-esteem, particularly in adolescence |
Also Read: 49 Difference between Acne and Rosacea
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQS)
Q.1 What causes acne?
Overproduction of sebum (skin oil) and buildup of dead skin cells and bacteria in hair follicles cause acne. This causes blocked pores, which can cause pimples, blackheads, and zits.
Q.2 What's the difference between over-the-counter and prescription acne treatments?
OTC acne remedies are for mild to severe acne and have lower active ingredient concentrations. These products usually contain benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or alpha hydroxy acids. For severe acne, prescription treatments with retinoids, antibiotics, or oral medicines are advised.
Q.3 Are there any lifestyle factors that contribute to acne development?
Several lifestyle factors might cause acne. Hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy cause acne. Diet, especially high-glycemic-index meals and dairy, may contribute. Stress, poor skincare, and comedogenic products can worsen acne.
Q.4 Can picking or squeezing acne worsen the condition?
Picking or squeezing acne can cause infection, scarring, and bacteria spread. It might also delay healing and cause additional acne. Avoid touching or manipulating acne and use correct skincare and therapy.
Q.5 How can I prevent acne and promote healthy skin?
A steady skincare routine prevents acne. Use non-comedogenic moisturizers and sunscreens and wash your face twice a day with a gentle cleanser. Weekly exfoliation removes dead skin cells. Avoid facial touching and use oil-free cosmetics and skincare. Stay hydrated and eat a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. If acne continues, consult a dermatologist for customized therapy.