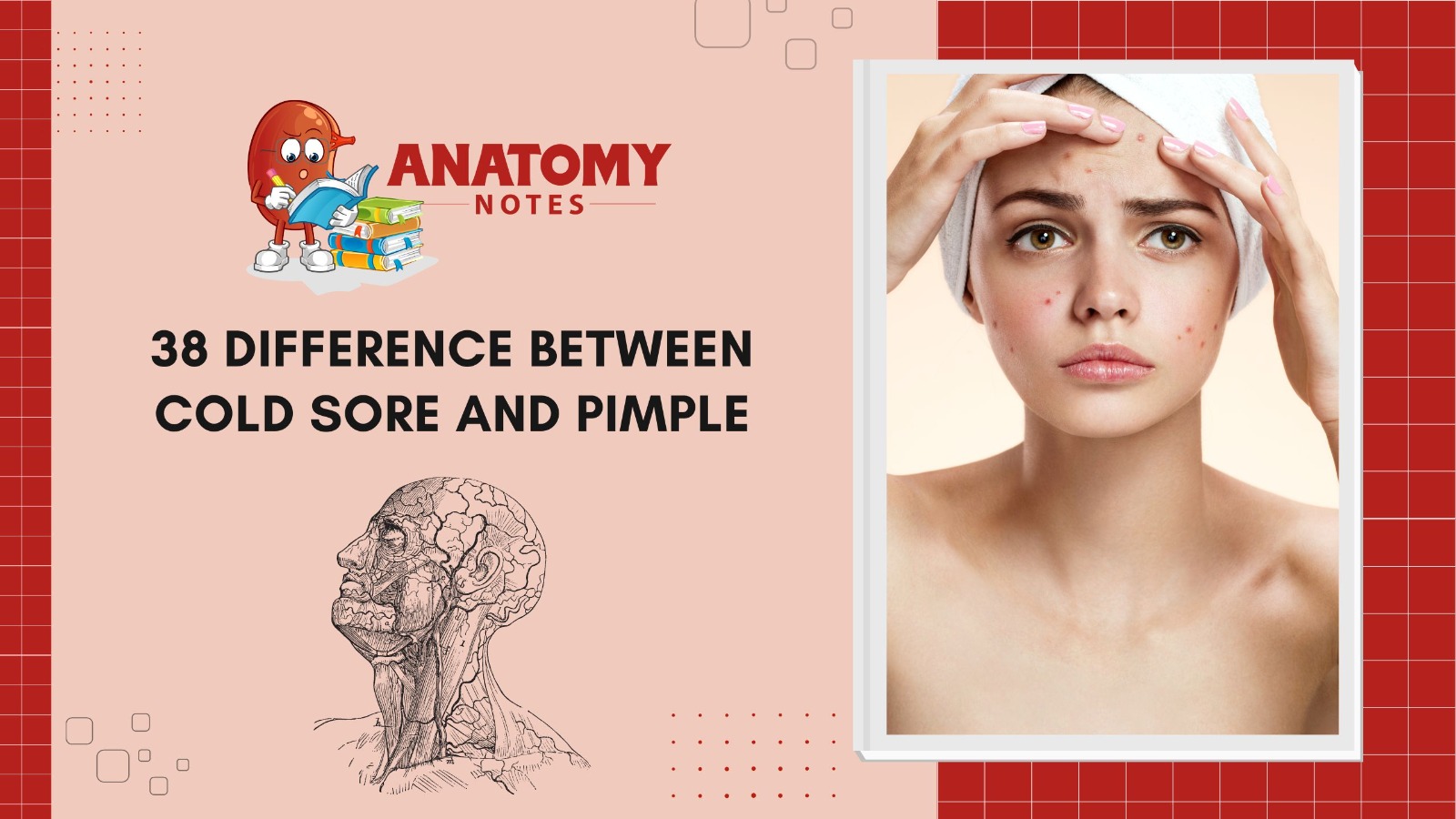
Cold sores and pimples are frequent skin disorders with different origins, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding the main distinctions might help people manage their skin issues. Cold sores (fever blisters) are produced by the herpes simplex virus. These little clusters of fluid-filled blisters usually develop around the lips, although they can also form on the gums, mouth, or nostrils. Kissing or sharing utensils can spread cold sores, which are infectious. Before blisters form, they cause stinging, burning, or tingling. Blisters burst, crust, and heal. Antivirals lessen cold sore length and intensity.
However, clogged hair follicles and increased oil production cause pimples. They can appear everywhere, but the face, neck, back, and chest are most prevalent. Red, pus-filled pimples are caused by inflammation. Hormonal changes, Propionibacterium acnes, and abundant sebum can cause them. Picking or squeezing pimples can exacerbate the disease and scar. Maintaining appropriate cleanliness, utilizing topical benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid treatments, and seeing a dermatologist for prescription drugs will help pimples.
Cold sores and pimples have different origins, appearances, and treatments. The herpes simplex virus causes cold sores, which are fluid-filled blisters around the lips. They need antivirals and are infectious. However, clogged hair follicles and excessive oil production cause pimples, which are red, inflammatory lumps packed with pus. For pimples, cleanliness and topical treatments are crucial. Differentiating cold sores from pimples is essential for proper treatment. Consult a doctor or dermatologist if unsure about a skin lesion. Good cleanliness, avoiding cold sore sores, and not picking pimples can also improve skin health and prevent infection.
Also Read: 49 Difference between Acne and Rosacea
Here are the 38 differences between a Cold Sore (Herpes Labialis) and a Pimple:
|
S.No. |
Aspects |
Cold Sore (Herpes Labialis) |
Pimple |
|
1 |
Medical Condition |
Viral infection caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). |
Inflammatory skin condition caused by clogged hair follicles. |
|
2 |
Location |
Typically appears on or around the lips, but can occur near the mouth or on the face. |
Can occur anywhere on the body, most commonly on the face, neck, chest, and back. |
|
3 |
Causative Agent |
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). |
Bacteria, particularly Propionibacterium acnes, and sometimes Staphylococcus aureus. |
|
4 |
Transmission |
Usually spreads through direct contact with an infected person or sharing items like utensils or towels. |
Not contagious; not transmitted through contact with others. |
|
5 |
Contagiousness |
Highly contagious when active lesions are present. |
Not contagious to others. |
|
6 |
Appearance |
Small, fluid-filled blisters or sores often grouped together. |
Red, raised bump with a white or yellow center. |
|
7 |
Fluid Inside Lesion |
Contains clear or yellowish fluid filled with the virus. |
Contains pus, white blood cells, and bacteria. |
|
8 |
Pain or Itchiness |
Can be painful or itchy, especially during the initial outbreak. |
May be tender, itchy, or painful. |
|
9 |
Duration of Lesion |
Typically lasts 7-10 days but can persist longer. |
May last a few days to a week or more, depending on severity. |
|
10 |
Causes Recurring Outbreaks |
Can recur periodically, especially during times of stress or illness. |
Occasional pimples may recur, but not as frequently as cold sores. |
|
11 |
Trigger Factors |
Stress, illness, exposure to sunlight, hormonal changes. |
Hormonal changes, excess oil production, and skin irritation. |
|
12 |
Associated Symptoms |
Fever, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes (during initial outbreak). |
No systemic symptoms unless a pimple becomes infected. |
|
13 |
Viral Shedding |
Active cold sores can shed the herpes virus and be contagious even without visible sores. |
Pimples do not shed infectious agents. |
|
14 |
Diagnosis |
Based on appearance and clinical evaluation; can be confirmed through lab tests. |
Usually diagnosed by appearance and medical history; no specific lab test needed. |
|
15 |
Treatable |
Antiviral medications (e.g., acyclovir) can help manage and reduce symptoms. |
Can be treated with topical or oral antibiotics in case of infection. |
|
16 |
Prevention |
Avoid close contact with active cold sores; use lip balm with SPF to prevent sun-triggered outbreaks. |
Maintain good hygiene and skincare practices; avoid picking or squeezing pimples. |
|
17 |
Risk of Scarring |
Rarely leaves scarring unless the sores are repeatedly irritated. |
Pimples can leave scars, especially when picked or squeezed. |
|
18 |
Associated Virus Type |
HSV-1 is the primary cause, but HSV-2 (genital herpes) can also cause oral herpes. |
Not associated with viral infection. |
|
19 |
Sexually Transmitted |
Can be sexually transmitted when oral-genital contact occurs. |
Not a sexually transmitted condition. |
|
20 |
Immune System Involvement |
The immune system plays a role in controlling and suppressing herpes outbreaks. |
The immune system may affect the frequency and severity of pimples. |
|
21 |
Over-the-Counter Products |
Lip balms and creams may provide symptomatic relief. |
Over-the-counter acne products may help treat pimples. |
|
22 |
Age of Onset |
Can occur at any age, including childhood. |
Most commonly begins during adolescence but can occur at any age. |
|
23 |
Risk of Spreading to Eyes |
Can spread to the eyes, causing ocular herpes (rare). |
Generally does not spread to the eyes. |
|
24 |
Risk of Complications |
Can lead to complications like herpetic whitlow (finger infection) or eczema herpeticum (widespread infection). |
Pimples can become infected but typically do not lead to severe complications. |
|
25 |
Risk During Pregnancy |
Pregnant women with active cold sores may transmit the virus to their newborn (neonatal herpes). |
Pimples do not pose a risk to pregnancy. |
|
26 |
Treatment During Pregnancy |
Antiviral medications may be prescribed for pregnant women with active cold sores. |
Topical treatments for pimples are generally considered safe during pregnancy. |
|
27 |
Associated Painful Sensation |
Can be painful, especially when the sores are ruptured or irritated. |
May be painful if inflamed or infected. |
|
28 |
Frequency of Occurrence |
Can recur multiple times a year. |
Pimples can occur sporadically but may be more common during adolescence. |
|
29 |
Autoinoculation |
Can spread to other areas of the body (autoinoculation) if precautions are not taken. |
Pimples do not typically spread to other areas of the body. |
|
30 |
Treatment for Autoinoculation |
Antiviral medications may be used to prevent autoinoculation. |
Not applicable to pimples. |
|
31 |
Risk of Complications in Newborns |
Neonatal herpes can be severe and life-threatening in newborns. |
Pimples do not pose a risk to newborns. |
|
32 |
Protection Methods |
Avoid kissing or oral-genital contact during an outbreak to prevent transmission. |
Avoid picking or squeezing pimples to prevent infection and scarring. |
|
33 |
Treatment for Primary Infection |
Antiviral medications are used to treat primary herpes infections. |
Pimples may resolve without specific treatment. |
|
34 |
Vaccination Availability |
No specific vaccine for cold sores, but vaccines for herpes are in development. |
No vaccination for pimples; it is not a viral condition. |
|
35 |
Hereditary Factors |
Can be associated with a family history of herpes outbreaks. |
Not hereditary; not passed down genetically. |
|
36 |
Immune System Suppression |
Outbreaks may occur more frequently in individuals with weakened immune systems. |
Immune system suppression can increase the risk of acne. |
|
37 |
Relapse After Treatment |
Outbreaks may recur after treatment but are often less severe. |
Pimples can return if the underlying causes persist. |
|
38 |
Impact on Emotional Well-being |
May cause emotional distress due to stigma and visible lesions. |
Can affect self-esteem but usually less stigmatized than cold sores. |
Also Read: 29 Difference between Heat Stroke and Heat Exhaustion
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQS)
Q.1 What causes cold sores and how are they different from pimples?
HSV-1 causes cold sores. Clusters of fluid-filled blisters surround the lips or mouth. However, clogged hair follicles and increased oil production cause red, inflammatory, pus-filled pimples. Pimples are produced by hormonal fluctuations and bacteria, whereas cold sores are communicable and viral.
Q.2 Are cold sores and pimples transferable?
Cold sores spread easily. Kissing, sharing utensils, or touching an infected region can transmit HSV. However, pimples are not communicable. Hormonal abnormalities and microbes cause them, and casual contact seldom spreads them.
Q.3 What treatments are available for cold sores and pimples?
Topical and oral antivirals help minimize the intensity and duration of cold sores. Symptom alleviation may also come from OTC creams. For pimples, use good skincare. Over-the-counter benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid topicals can cure mild instances. Dermatologists may give antibiotics or retinoids for severe instances.
Q.4 Can I pop a cold sore or pimple?
Avoid popping cold sores and pimples. Popping cold sores can transfer the infection to other skin or persons. Popping pimples increases inflammation, infection, and scarring. Consult a doctor for a pimple or cold sore therapy.
Q.5 Can I avoid cold sores and pimples?
Avoid close touch with cold sore sufferers to prevent them. A balanced diet, frequent exercise, and stress management can also minimize breakouts. Wash your face gently with a light cleanser and avoid over-scrubbing to avoid pimples. Use non-comedogenic skincare and prevent filthy hands and face. For severe acne, see a dermatologist for personalized therapy.