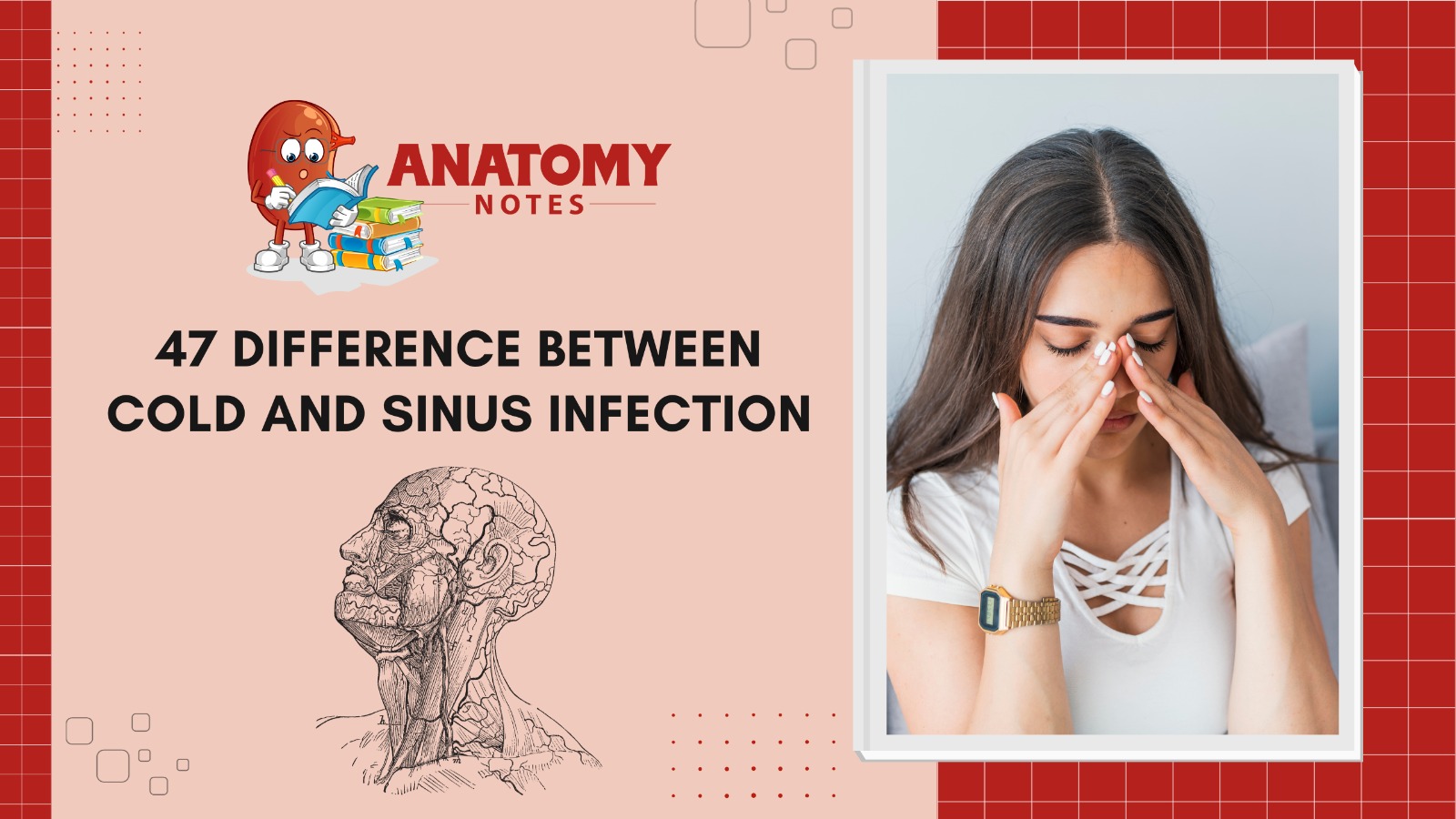
Common respiratory illnesses like colds and sinus infections cause pain and congestion. They have different causes, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding these differences can help people manage their symptoms and get medical aid. A cold, or common cold, is caused by viruses such as rhinoviruses. It causes runny or stuffy noses, sneezing, sore throats, coughing, and minor lethargy or headaches. The symptoms normally develop gradually and last a week before improving.
Cold symptoms can be treated with over-the-counter medicines, rest, and water. Colds are viral, thus antibiotics don’t work. Sinusitis, on the other hand, is caused by inflammation or infection of the sinus cavities, air-filled openings in the face bones. Sinus infections can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or allergies. Sinus infections cause a worse headache, face discomfort or pressure, nasal congestion, and impaired sense of smell.
Unlike colds, sinus infections can cause fever. Sinus infections may be treated with over-the-counter painkillers, decongestants, saline nasal sprays, and antibiotics if a bacterial infection is detected. The duration and intensity of symptoms distinguish a cold from a sinus infection. Sinus infections last more than 10 days, unlike colds, which peak within a few days and recover over a week. Clear, watery nasal discharge is typical of colds, but thicker, discolored discharge is typical of sinus infections.
In conclusion, distinguishing cold from a sinus infection is essential for treatment. Colds are viral diseases that relieve minor symptoms in a week with rest and fluids. Inflammation or infection of the sinus cavities causes face discomfort, nasal congestion, and fever. Some illnesses require over-the-counter medicines, nasal sprays, and antibiotics. If symptoms are severe, persistent, or worsen over time, see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Also Read: A Guide to Kidneys: Size, Structure, Function & More
Here are 47 differences between a cold and a sinus infection:
|
S.No. |
Aspects |
Cold |
Sinus Infection (Sinusitis) |
|
1 |
Medical Term |
Common cold |
Sinusitis |
|
2 |
Causative Agents |
Viruses (most commonly rhinoviruses) |
Viruses (commonly, but can also be bacterial) |
|
3 |
Onset |
Gradual onset |
Symptoms may develop more suddenly |
|
4 |
Duration |
Typically lasts 7-10 days |
Can last longer (more than 10 days) |
|
5 |
Primary Symptoms |
Runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, sore throat |
Nasal congestion, facial pain or pressure, discolored mucus |
|
6 |
Fever |
Rarely causes a fever |
Can be associated with fever |
|
7 |
Headache |
Often associated with sinus headache |
|
|
8 |
Cough |
Dry or mild cough |
May have a productive cough |
|
9 |
Fatigue |
Mild fatigue |
Can cause significant fatigue |
|
10 |
Sore Throat |
Commonly associated |
May or may not be present |
|
11 |
Facial Pain or Pressure |
Rarely associated |
Commonly associated |
|
12 |
Nasal Congestion |
Common, but typically mild |
Severe nasal congestion is common |
|
13 |
Loss of Taste or Smell |
Possible loss of taste and smell |
Commonly affects taste and smell |
|
14 |
Chest Congestion |
Generally not associated |
Generally not associated |
|
15 |
Sinus Drainage |
Mild sinus drainage |
Excessive sinus drainage |
|
16 |
Breathing Difficulty |
Rarely causes significant breathing difficulty |
May cause difficulty in breathing |
|
17 |
Coughing Up Mucus |
May cough up clear or white mucus |
May cough up discolored or greenish mucus |
|
18 |
Treatment |
Rest, hydration, over-the-counter cold remedies |
May require antibiotics for bacterial sinusitis |
|
19 |
Antibiotics |
Not effective (colds are viral) |
May be prescribed if bacterial infection is present |
|
20 |
Contagiousness |
Highly contagious |
Can be contagious, especially in the early stages |
|
21 |
Seasonal Patterns |
More common in colder months |
Can occur year-round, not necessarily seasonal |
|
22 |
Complications |
Uncommon complications |
Can lead to complications like chronic sinusitis |
|
23 |
Recurrence |
Frequent recurrence is common |
May recur, especially with chronic sinusitis |
|
24 |
Prevention |
Handwashing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals |
Allergy management, avoiding triggers, treating underlying causes |
|
25 |
Allergies |
Not typically related to allergies |
Allergies can contribute to sinusitis |
|
26 |
Severity of Symptoms |
Mild to moderate symptoms |
Symptoms can range from mild to severe |
|
27 |
Triggers |
Viral exposure, weakened immune system |
Viral or bacterial infection, allergies, structural issues |
|
28 |
Complicating Factors |
Rarely leads to complications |
Can lead to chronic sinusitis or other complications |
|
29 |
Need for Medical Attention |
Typically not required |
May require medical evaluation and treatment |
|
30 |
Diagnostic Tests |
Usually diagnosed based on symptoms |
May require imaging (CT scan) for diagnosis |
|
31 |
Sinus Discharge Color |
Clear or white |
Can be green or discolored |
|
32 |
Pain Location |
Generally minimal facial pain |
Pain often localized to the sinuses |
|
33 |
Severity of Facial Pain |
Rarely causes severe facial pain |
Can cause intense facial pain |
|
34 |
Mucus Consistency |
Usually clear or thin mucus |
May have thick and discolored mucus |
|
35 |
Nasal Irrigation |
Not typically needed |
Nasal irrigation may be helpful |
|
36 |
Potential Complications |
Unlikely to cause severe complications |
Can lead to chronic sinusitis or spread to nearby areas |
|
37 |
Response to Antiviral Medications |
Not effective against cold viruses |
Antiviral medications may be effective for viral sinusitis |
|
38 |
Location of Symptoms |
Symptoms can affect the nose, throat, and upper respiratory tract |
Symptoms primarily affect the sinuses and nasal passages |
|
39 |
Immune Response |
Typically resolved by the immune system |
May require the immune system to fight infection |
|
40 |
Common Remedies |
Rest, fluids, over-the-counter cold remedies |
Antibiotics (if bacterial), decongestants, saline nasal sprays |
|
41 |
Age Groups Affected |
Affects people of all ages |
Can affect people of all ages, including children |
|
42 |
Allergic Rhinitis |
Not typically related to allergic rhinitis |
May be exacerbated by allergic rhinitis |
|
43 |
Risk Factors |
Close contact with infected individuals |
Allergies, previous sinus infections, structural issues |
|
44 |
Complications in Children |
Generally mild in children |
Can be more severe in children |
|
45 |
Complications in Older Adults |
Generally mild in older adults |
Can be more severe in older adults |
|
46 |
Immune Response Time |
Usually resolves within a week or two |
May persist for an extended period |
|
47 |
Chronic Conditions |
Rarely leads to chronic conditions |
Can result in chronic sinusitis if not properly managed |
Also Read: 18 Differences between acute and chronic pancreatitis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQS)
Q.1 What is the main difference between a cold and a sinus infection?
Their main differences are causal agents and symptom severity. Colds, caused by viruses like rhinoviruses, induce moderate symptoms including a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, and coughing. Sinusitis can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi. They have more severe symptoms such as face discomfort, pressure, headaches, and discolored nasal discharge.
Q.2 How can I tell a viral sinus infection from a bacterial one?
Spotting the difference might be difficult, but indications can assist. Bacterial sinus infections are more common if you have thick green or yellow nasal discharge, face discomfort, and fever for more than 10 days. A cold or other viral sickness may cause viral sinus infections, which usually heal within a week.
Q.3 Can colds cause sinus infections?
Yes, colds can cause sinus infections. Colds can produce nasal irritation and congestion, causing sinus obstructions. Blocked sinuses can proliferate germs, causing subsequent sinus infections.
Q.4 When should I visit a doctor for a cold or sinus infection?
A cold seldom requires medical treatment unless symptoms are severe or persistent. If you have significant face discomfort, high fever, increasing symptoms after a week, or symptoms lasting more than 10 days, see a doctor for a sinus infection evaluation. Bacterial sinus infections may need antibiotics.
Q.5 How can I avoid colds and sinuses?
The best way to avoid colds is to wash your hands often, avoid ill people, and get vaccinated. Manage allergies, treat colds quickly, and avoid irritants like cigarette smoke and pollution to avoid sinus infections.