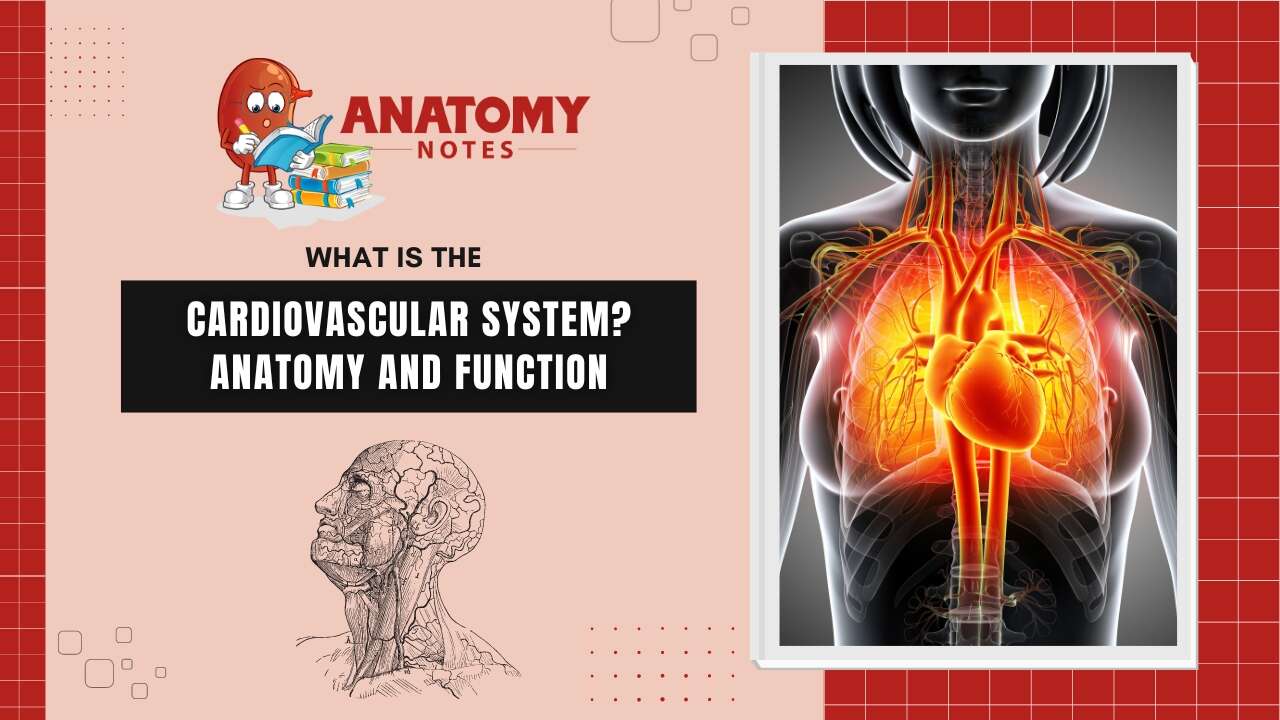
The cardiovascular system is the transport system of our body in which cardio refers to heart and vascular refers to blood vessels.
The basic purpose of the cardiovascular system is to circulate the blood to the cell from cells in the body in order to transport nutrients and remove waste.
Hence it is also known as the circulatory system. There are three main components of the cardiovascular system which are as follows:-
The heart, whose pumping action ensures the constant circulation of the blood.
The heart is a roughly cone-shaped hollow muscular organ. It is about 10 cm long and is about the size of the owner’s fist.
It weighs about 225 g in women and is heavier in men (about 310 g). The heart lies in the thoracic cavity in the mediastinum (the space between the lungs).
It lies obliquely, a little more to the left than the right, and presents a base above, and an apex below.
The apex is about 9 cm to the left of the midline at the level of the 5th intercostal space, i.e. a little below the nipple and slightly nearer the midline.
The base extends to the level of the 2nd rib. The heart wall is composed of three layers of tissue pericardium, myocardium, and endocardium.
The blood vessels, which form a lengthy network through which the blood flows.
The blood vessels vary in structure, size and function, and there are several types: arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins.
Arteries
- These blood vessels transport blood away from the heart.
- They vary considerably in size and their walls consist of three layers of tissue which are listed below:-
- Tunica adventitia or outer layer of fibrous tissue
- Tunica a media or middle layer of smooth muscle and elastic tissue.
- Tunica intima or inner lining of squamous epithelium called endothelium
Arterioles
Arteries branch many times and become smaller until in the arterioles (the smallest arteries) the tunica media consists entirely of smooth muscles and it can control the blood flow to capillary.
Capillaries
The smallest arterioles break up into a number of minute vessels called capillaries.
Venules
The smallest vein is known as venules.
Veins
Veins return blood at low pressure to the heart. The walls of the veins are thinner than arteries but have the same three layers of tissue.
They are thinner because there is less muscle and elastic tissue in the tunica media, as veins carry blood at a lower pressure than arteries.
When cut, the veins collapse while the thicker-walled arteries remain open.
When an artery is cut blood spurts at high pressure while a slower, steady flow of blood escapes from a vein.
The blood itself, blood is a fluid that contains the oxygen and nutrients the body needs and carries the wastes which need to be removed.
Here we trying to present the basic understanding of the cardiovascular system.
The heart has two major circuits within the circulatory pathway.
They worked together in a closed circulatory system. These two pathways are listed below :
The pulmonary circulation
- In pulmonary circulation, the right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs (the pulmonary circulation) where gas exchange occurs, i.e. the blood collects oxygen from the air sacs and excess carbon dioxide diffuses into the air sacs for exhalation.
The systemic circulation
- In the systemic circulation, the left side of the heart pumps blood, which supplies the rest of the body.
- Here, tissue wastes are passed into the blood for excretion, and body cells extract nutrients and oxygen.
Functions of the cardiovascular system
Blood circulates through a network of vessels throughout the body to provide individual cells with oxygen and nutrients and helps dispose of metabolic wastes. The heart pumps the blood around the blood vessels.
Functions of blood and circulation
- Circulates OXYGEN and removes Carbon Dioxide.
- It provides cells with NUTRIENTS.
- Removes the waste products of metabolism to the excretory organs for disposal.
- Protects the body against disease and infection.
- Clotting stops bleeding after an injury.
- Transports HORMONES to target cells and organs.
- It helps regulate body temperature.
Cardiovascular function normally declines with age.
The disease of the cardiovascular system is likely to have significant consequences, not only for the heart and blood vessels but also for other body systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the cardiovascular system ?
The cardiovascular system is a vital organ system in the human body that is responsible for transporting blood, oxygen, and nutrients throughout the body. The cardiovascular system comprises of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.. The heart pumps blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen and then pumps it to the rest of the body through arteries, capillaries, and veins. The cardiovascular system plays a critical role in maintaining homeostasis and overall health.
What are the 4 main functions of the cardiovascular system?
There are four primary functions of the cardiovascular system, which include:
- Transportation: The cardiovascular system is responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
- Regulation: The cardiovascular system helps regulate blood pressure, body temperature, and pH balance.
- Protection: The cardiovascular system plays a critical role in the immune response by transporting white blood cells and antibodies to fight infection and disease.
- Clotting: The cardiovascular system helps to form blood clots to prevent excessive bleeding when blood vessels are damaged.
What is the function of heart?
The primary role of the heart is to circulate blood throughout the body by pumping it through the cardiovascular system. It is a muscular organ that receives oxygen-poor blood from the body through the veins and pumps it to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The oxygen-rich blood is then returned to the heart, which pumps it out to the rest of the body through the arteries.
What is the largest artery in the body?
In terms of size, the largest artery present in the human body is the aorta. It is the main artery that originates from the left ventricle of the heart and carries oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body. The aorta is about the size of a garden hose and runs from the heart down through the chest and abdomen before dividing into smaller arteries that supply blood towards the different organs and tissues located in the body. Due to its important role in the cardiovascular system, any damage or disease affecting the aorta can have serious consequences for overall health.
Which component of the cardiovascular system holds the most significance?
All components of the cardiovascular system are essential for its proper functioning, and each plays a critical role in maintaining overall health. However, the most important part of the cardiovascular system is the heart. The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, providing oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and removing waste products. It is responsible for maintaining blood pressure and regulating blood flow, and it plays a crucial role in the functioning of the entire cardiovascular system.
What are the diseases of cardiovascular?
- Coronary artery disease (CAD): This occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart, leading to reduced blood flow and oxygen to the heart muscle.
- Heart attack: A heart attack occurs when there is a sudden blockage of blood flow to the heart, usually due to a blood clot forming in a coronary artery.
- Stroke: A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, usually due to a blood clot or a burst blood vessel.
- Heart failure: When the heart cannot pump sufficient blood to satisfy the body’s demands, this condition is referred to as heart failure.
- Arrhythmias: These are abnormal heart rhythms that can range from harmless to life-threatening.
- Aortic aneurysm: Refers to the enlargement or swelling of the aorta, which is the primary blood vessel responsible for carrying blood from the heart to other parts of the body.