Introduction to Amniotic Fluid
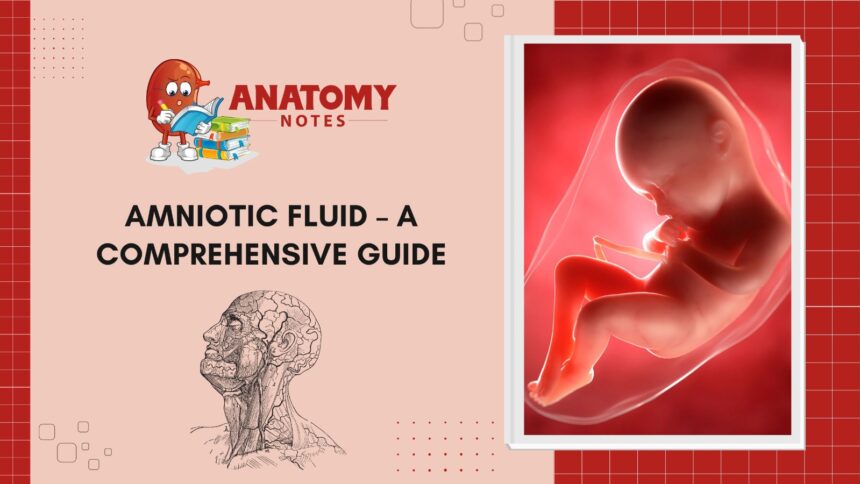
Welcome to a deep dive into the fascinating world of amniotic fluid – the unsung hero of pregnancy! This clear, slightly yellowish liquid plays a crucial role in nurturing and protecting your growing baby. Let’s explore everything you need to know about this remarkable substance that surrounds and supports your little one during their time in the womb.
Composition of Amniotic Fluid
Amniotic fluid is a complex mixture that plays a crucial role in supporting fetal growth and development throughout pregnancy. This clear, slightly yellowish liquid is mainly composed of water, electrolytes, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and hormones. The exact composition can vary depending on the stage of pregnancy and the health of the mother and fetus.
Proteins such as albumin and globulins help regulate osmotic balance and provide essential nutrients to the developing baby. Carbohydrates like glucose serve as an energy source for fetal metabolism. Lipids are important for cell membrane formation and hormone production.
Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, chloride, and magnesium help maintain proper fluid balance in the amniotic sac. Hormones like cortisol aid in lung maturation while growth factors support tissue development. Understanding the intricate composition of amniotic fluid gives us insight into its vital role in prenatal health.
Formation and Development
Amniotic fluid, a vital component of pregnancy, is formed early in gestation. Initially, it consists mainly of water from maternal circulation that passes through the placenta into the amniotic sac. As the pregnancy progresses, fetal urine also contributes to the volume and composition of the fluid.
The development of amniotic fluid is closely linked to fetal kidney function. Around week 16 of gestation, the fetus begins producing urine which helps maintain appropriate levels of amniotic fluid. The amniotic sac continuously adjusts its volume by selectively reabsorbing or excreting components to ensure a suitable environment for fetal growth and development.
As pregnancy advances, the formation and turnover rate of amniotic fluid increase significantly. This dynamic process plays a crucial role in protecting and nurturing the developing fetus throughout each stage of prenatal development.
Functions of Amniotic Fluid
Amniotic fluid plays a crucial role in supporting the development of the fetus throughout pregnancy. It acts as a cushion, protecting the baby from external impacts while also allowing for movement and growth. Additionally, amniotic fluid helps maintain a stable temperature within the womb, keeping the fetus comfortable and safe.
Furthermore, this fluid serves as a barrier against infections by providing an environment that is sterile and free from harmful microorganisms. Amniotic fluid also aids in lung development by allowing the fetus to practice breathing movements while still in utero.
Moreover, it facilitates nutrient exchange between mother and baby, ensuring that essential substances like oxygen and hormones reach the developing fetus efficiently. In essence, amniotic fluid is not just water surrounding the baby—it’s a vital substance that nurtures and sustains life within the womb.
Volume Changes During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the volume of amniotic fluid undergoes significant changes as your baby grows and develops inside the womb. Initially, the amniotic fluid is produced by the mother’s placenta and later by the fetal kidneys. As your pregnancy progresses, the volume steadily increases to accommodate your growing baby.
Around 20 weeks gestation, there is approximately 800ml of amniotic fluid present, reaching its peak at about 28 weeks with around 1000ml to 1500ml. This optimal amount provides cushioning for your baby and allows them to move freely while also helping maintain a stable temperature in utero.
In late pregnancy, usually around term (37-40 weeks), the volume starts decreasing slightly as some of it gets reabsorbed or expelled through fetal swallowing and urination. This gradual reduction in amniotic fluid helps prepare for labor and delivery when your baby will be born into a drier environment outside the womb.
It’s fascinating how these volume changes play a crucial role in supporting your baby’s growth and development throughout pregnancy.
Amniotic Fluid and Fetal Development
Amniotic fluid plays a crucial role in the development of the fetus throughout pregnancy. It provides protection, cushioning, and support to the growing baby inside the womb. The amniotic fluid also helps regulate the temperature and allows for fetal movement, which is essential for muscle and bone development.
Furthermore, amniotic fluid contains various nutrients that are important for fetal growth and development. These nutrients help nourish the baby while also aiding in lung maturation by allowing them to practice breathing movements. In addition, amniotic fluid assists in preventing compression of the umbilical cord, ensuring proper blood flow between mother and baby.
As pregnancy progresses, the volume of amniotic fluid increases to accommodate the growing fetus. This expansion is necessary for fetal lung development as it allows room for proper breathing movements before birth. Amniotic fluid plays a vital role in supporting healthy fetal development from conception to delivery.
Assessment of Amniotic Fluid Levels
When it comes to pregnancy, monitoring the levels of amniotic fluid is crucial for assessing the health and development of the baby.
Healthcare providers use various techniques to measure amniotic fluid levels, such as ultrasound scans and amniotic fluid index (AFI) measurements. These methods help determine if there is too much or too little amniotic fluid present.
An AFI measurement evaluates the pockets of fluid surrounding the baby in different quadrants of the uterus. This assessment helps healthcare professionals gauge whether the volume of amniotic fluid is within a normal range.
Changes in amniotic fluid levels can indicate potential issues with fetal well-being, such as intrauterine growth restriction or placental dysfunction. Regular monitoring allows for timely interventions if abnormalities are detected.
Keeping track of amniotic fluid levels plays a vital role in ensuring a healthy pregnancy and safe delivery for both mother and baby.
Abnormalities in Amniotic Fluid
Abnormalities in amniotic fluid can pose risks during pregnancy. Low levels, known as oligohydramnios, may indicate fetal distress or developmental issues. On the other hand, excess amniotic fluid, called polyhydramnios, could suggest conditions like gestational diabetes or neural tube defects.
Monitoring amniotic fluid levels through ultrasound scans is crucial to identify any abnormalities early on. In some cases, medical interventions such as amnioinfusion or drainage may be necessary to manage imbalances and ensure the well-being of both mother and baby.
It’s essential for healthcare providers to closely monitor changes in amniotic fluid volume throughout pregnancy to prevent complications and make informed decisions about care. Early detection and management of abnormalities can significantly impact the outcome of a pregnancy.
Amniocentesis and Diagnostic Uses
Amniocentesis is a diagnostic procedure where a small amount of amniotic fluid is extracted for testing. This test is typically done between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy to detect genetic disorders, chromosomal abnormalities, or neural tube defects in the fetus. It involves inserting a thin needle through the mother’s abdomen into the amniotic sac under ultrasound guidance.
The extracted fluid contains fetal cells that can be analyzed for various genetic conditions. Results from amniocentesis can provide valuable information to expectant parents about their baby’s health and development. While the procedure carries some risks such as infection or leakage of amniotic fluid, it is generally considered safe when performed by experienced healthcare providers.
Amniocentesis plays a crucial role in prenatal care by offering insights into potential health issues that may affect the baby. It allows parents to make informed decisions regarding their pregnancy and prepare for any necessary medical interventions.
Amniotic Fluid in Labor and Delivery
During labor and delivery, the amniotic fluid plays a crucial role in protecting the baby as it makes its way through the birth canal. The amniotic sac helps cushion the baby from external pressure during contractions. This fluid also provides lubrication, making it easier for the baby to move down the birth canal.
As labor progresses, the amniotic sac may rupture naturally, leading to what is commonly known as a woman’s “water breaking.” This signifies that labor is imminent or already underway. In some cases, healthcare providers may need to artificially rupture the membranes to help speed up labor.
The presence of ample amniotic fluid during delivery is essential for ensuring smooth passage of the baby. It also helps maintain a sterile environment in which both mother and child are protected from potential infections.
Understanding how amniotic fluid functions during labor and delivery can provide reassurance to expectant mothers about this natural process.
Postpartum Considerations
Postpartum considerations are essential for the well-being of both the mother and baby after delivery. During this period, it’s crucial to monitor the mother’s physical and emotional health as she transitions into her new role. Adequate rest, proper nutrition, and support from family and healthcare providers play a significant role in postpartum recovery.
It’s common for new mothers to experience mood swings, fatigue, and changes in their body post-delivery. Understanding these changes and seeking help if needed is vital for a smooth recovery process. Additionally, bonding with the newborn through skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding promotes emotional attachment between mother and baby.
Monitoring any signs of infection or complications post-birth is crucial for early intervention if needed. It’s important to attend follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to ensure that both mother and baby are progressing well during the postpartum period.
Recent Research and Future Directions
Recent research in the field of amniotic fluid has revealed fascinating new insights into its role during pregnancy. Scientists are exploring how changes in the composition of amniotic fluid may impact fetal development and overall maternal health.
One exciting direction is the investigation of using amniotic fluid as a source of stem cells for potential regenerative medicine applications. This could revolutionize treatment options for various conditions in both pregnant women and newborns.
Researchers are also delving into the link between abnormal levels of amniotic fluid and certain pregnancy complications, such as preterm birth or fetal abnormalities. Understanding these associations can lead to improved monitoring strategies and intervention methods.
Future directions aim to further enhance our understanding of how environmental factors, maternal health, and genetic influences interact with amniotic fluid dynamics throughout pregnancy. By continuing to push boundaries through innovative research, we can unlock even more mysteries surrounding this vital substance.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of amniotic fluid, it’s clear that this remarkable substance plays a crucial role throughout pregnancy. From providing protection and cushioning for the developing fetus to aiding in fetal lung development, the importance of amniotic fluid cannot be overstated.
Looking towards the future, ongoing research into the composition and functions of amniotic fluid holds promising potential. Scientists are continuously uncovering new insights that could lead to improved prenatal care and diagnostic techniques.
While there is still much to learn about this fascinating fluid, one thing remains certain – its significance in nurturing and supporting life within the womb is undeniable. As we continue to delve deeper into the complexities of amniotic fluid, we can look forward to further advancements in prenatal medicine and maternal health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Got more questions about amniotic fluid? Here are some common queries answered:
Q1. How is the volume of amniotic fluid measured during pregnancy?
Healthcare providers use ultrasound to estimate the volume of amniotic fluid around the baby.
Q2. What can cause abnormalities in amniotic fluid levels?
Various factors like maternal health conditions, fetal abnormalities, or ruptured membranes can lead to abnormal levels of amniotic fluid.
Q3. Is it safe to undergo an amniocentesis procedure?
Amniocentesis is generally considered safe but does carry a small risk of complications. Your healthcare provider will discuss these risks with you before the procedure.
Have more questions? Consult your healthcare provider for personalized information and guidance on all things related to amniotic fluid. Stay informed and take care!