Introduction to Articular Cartilage
Welcome to the fascinating world of articular cartilage – the unsung hero that keeps our joints moving smoothly and pain-free! If you’ve ever wondered what exactly articular cartilage is and why it’s crucial for your joint health, you’re in the right place.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into everything you need to know about articular cartilage, from its structure and function to common issues affecting it and advances in regenerative medicine. So, let’s get ready to explore the amazing world of this essential tissue that plays a vital role in keeping us mobile and active!
Structure of Articular Cartilage
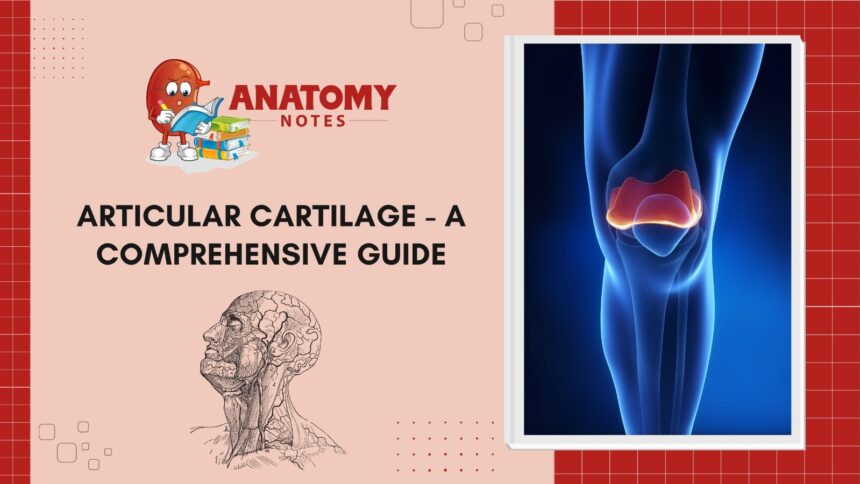
Articular cartilage is a remarkable structure within our joints that plays a crucial role in maintaining smooth movement and reducing friction during activities. It consists of specialized cells called chondrocytes, which are embedded in a matrix rich in collagen and proteoglycans. This unique composition gives articular cartilage its ability to absorb shock and provide cushioning between bones.
The structure of articular cartilage is divided into three distinct zones: the superficial zone, the transitional zone, and the deep zone. Each zone has specific characteristics that contribute to the overall function of the cartilage. The superficial zone contains flattened chondrocytes, while the transitional zone has a mix of round and elongated cells. In contrast, the deep zone consists of larger chondrocytes arranged in columns perpendicular to the joint surface.
This intricate structure allows articular cartilage to withstand mechanical stresses and maintain joint health throughout our daily movements. Understanding the complexity of its architecture helps us appreciate the importance of preserving this vital tissue for optimal joint function.
Function of Articular Cartilage in Joints
Articular cartilage plays a crucial role in our joints by providing a smooth, lubricated surface that allows for frictionless movement. Think of it as the cushion between bones that helps reduce wear and tear during daily activities. This specialized type of cartilage is designed to withstand pressure and distribute loads evenly across the joint.
Without articular cartilage, our joints would experience increased friction, leading to pain, stiffness, and potentially long-term damage. It acts as a shock absorber, absorbing impact forces during movements like walking, running, or jumping. Additionally, articular cartilage aids in maintaining joint stability and facilitating smooth motion without restrictions.
By promoting low-friction movement and distributing mechanical stresses evenly within the joint, articular cartilage ensures proper function while protecting the underlying bone from excessive strain. Its unique composition gives it exceptional durability and resilience to maintain joint health throughout life’s various activities.
Composition of Articular Cartilage
Articular cartilage is a remarkable tissue that plays a crucial role in our joints’ function and movement. Composed mainly of water, collagen fibers, and proteoglycans, articular cartilage has a unique structure that allows it to absorb shock and distribute loads efficiently.
The collagen fibers provide strength and flexibility to the cartilage, while the proteoglycans help maintain its elasticity and resilience. These components work together harmoniously to support smooth joint motion and reduce friction during movement.
In addition to its composition, articular cartilage also contains chondrocytes – specialized cells responsible for maintaining the extracellular matrix. These cells play a vital role in regulating the synthesis and degradation of key components within the cartilage structure.
Understanding the intricate composition of articular cartilage is essential in appreciating its importance in joint health and mobility.
Types of Cartilage in the Human Body
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found throughout the human body, providing structural support and cushioning in various areas. In addition to articular cartilage, there are two other types of cartilage present: hyaline cartilage and fibrocartilage.
Hyaline cartilage is the most abundant type in the body, appearing as a shiny blueish-white material on joint surfaces. It’s crucial for reducing friction between bones and facilitating smooth movement. Hyaline cartilage can be found in areas like the nose, ribs, trachea, and larynx.
On the other hand, fibrocartilage is tougher than hyaline cartilage due to its high collagen content. This type of cartilage acts as a shock absorber and is commonly located in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, and certain tendons.
Each type of cartilage plays a unique role in maintaining bodily functions and supporting overall health.
Importance of Articular Cartilage in Joint Health
Articular cartilage plays a crucial role in maintaining joint health. It acts as a cushion between bones, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement. Without healthy articular cartilage, joints can become stiff, painful, and prone to injuries.
The importance of articular cartilage becomes evident during activities that involve repetitive motion or weight-bearing exercises. It helps distribute the load evenly across the joint surface, preventing wear and tear on the bones. This protective function is essential for overall joint longevity and functionality.
Furthermore, articular cartilage contains no blood vessels or nerves of its own. It relies on nutrients from synovial fluid to stay nourished and hydrated. When this balance is disrupted due to injury or degeneration, it can lead to conditions like osteoarthritis.
Maintaining healthy articular cartilage through proper nutrition, exercise, and avoiding excessive stress on the joints is key to preserving joint health in the long term. Prioritizing care for this vital tissue can significantly impact overall mobility and quality of life.
Common Issues and Diseases Affecting Articular Cartilage
When it comes to articular cartilage, there are various common issues and diseases that can impact its health and function. One of the most well-known conditions is osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that affects millions worldwide. Osteoarthritis causes the breakdown of cartilage over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in affected joints.
Another issue that can affect articular cartilage is traumatic injury. Sports injuries or accidents can cause damage to the cartilage, resulting in pain and potential long-term complications if not properly treated. Additionally, inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can also target articular cartilage, causing inflammation and erosion of the tissue.
It’s essential to address these issues promptly through proper medical care, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to preserve joint health and prevent further damage. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding activities that put excessive strain on your joints can help protect your articular cartilage from these common ailments.
Regeneration and Repair of Articular Cartilage
Regeneration and repair of articular cartilage are essential processes in maintaining healthy joints. Unlike other tissues in the body, articular cartilage has a limited capacity for self-repair due to its avascular nature. When damaged, this type of cartilage can undergo slow healing or degenerate over time if not properly treated.
Research in regenerative medicine has led to advancements in techniques such as microfracture surgery, autologous chondrocyte implantation, and tissue engineering that aim to stimulate the regeneration of articular cartilage. These methods involve promoting the growth of new cartilage cells or replacing damaged tissue with engineered constructs.
Factors like age, injury severity, and overall joint health play significant roles in determining the success of these repair strategies. It is crucial for individuals to seek early intervention and follow recommended rehabilitation protocols to maximize their chances of successful cartilage regeneration.
With ongoing research and technological developments, scientists continue to explore innovative approaches for enhancing the repair process and improving outcomes for individuals with articular cartilage injuries. By staying informed about these advancements, patients can make more informed decisions regarding their treatment options for joint health maintenance.
Factors Affecting Articular Cartilage Health
Maintaining healthy articular cartilage is essential for optimal joint function and overall well-being. Several factors can impact the health of this crucial tissue.
One key factor is age, as cartilage tends to wear down over time due to natural aging processes. Additionally, genetics play a role in determining an individual’s predisposition to cartilage-related issues.
Physical activity levels also influence articular cartilage health – both excessive strain from high-impact activities and prolonged periods of inactivity can have negative effects.
Nutrition is another significant factor, with a diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supporting cartilage health. Conversely, poor dietary choices can contribute to inflammation and degradation of cartilage tissue.
Injuries such as fractures or dislocations can directly damage articular cartilage and impact its long-term health. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed choices to protect their joints and maintain healthy cartilage throughout life.
Comparison with Other Types of Cartilage
When it comes to cartilage in the human body, there are different types serving various functions. Articular cartilage, found at the ends of bones in joints, is unique compared to other types like hyaline or fibrocartilage.
Hyaline cartilage is present in areas where flexibility and support are needed, such as the ribs and respiratory tract. It has a smooth surface but lacks the cushioning properties of articular cartilage.
Fibrocartilage, on the other hand, is tougher and can be found in areas subjected to heavy pressure like intervertebral discs and knee menisci. It contains more collagen fibers than articular cartilage.
While all types of cartilage play crucial roles in our bodies’ structure and function, articular cartilage stands out for its ability to reduce friction between bones during movement while providing shock absorption.
Research and Advances in Cartilage Biology
Research and advances in cartilage biology have paved the way for exciting developments in the field of orthopedics. Scientists are continually exploring new techniques to enhance our understanding of cartilage structure and function. Through cutting-edge technologies, such as tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, researchers aim to revolutionize the treatment of cartilage-related conditions.
Stem cell therapy is a promising area of study that holds great potential for repairing damaged articular cartilage. By harnessing the regenerative abilities of stem cells, scientists are working towards creating innovative solutions for joint injuries and osteoarthritis. In addition, bioengineering approaches enable the development of synthetic materials that mimic natural cartilage properties.
Furthermore, advancements in molecular biology have shed light on key signaling pathways involved in cartilage development and maintenance. By unraveling these intricate mechanisms, researchers can identify novel targets for therapeutic interventions aimed at preserving joint health. Collaborative efforts between clinicians and scientists continue to drive progress in this dynamic field, offering hope for improved treatments for individuals suffering from cartilage disorders.
Conclusion: Maintaining Healthy Articular Cartilage
Maintaining healthy articular cartilage is essential for overall joint health and mobility. By incorporating regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in nutrients like vitamin C and collagen, and avoiding excessive strain on the joints, you can help support the integrity of your cartilage.
Staying hydrated is also crucial as water helps to lubricate and cushion the joints, reducing wear and tear on the cartilage. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate excess pressure on weight-bearing joints such as knees and hips.
Engaging in low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can help preserve cartilage while strengthening surrounding muscles for added joint support. Regularly stretching to maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness in the joints is equally important.
Prioritizing preventative care through lifestyle choices can go a long way in preserving articular cartilage integrity over time. Remember, small habits add up to significant impacts on joint health in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Have more questions about articular cartilage? Check out these commonly asked questions for more insights:
Q1. How does aging affect articular cartilage?
As we age, the wear and tear on our joints can lead to a decrease in the quality of articular cartilage. This may result in conditions like osteoarthritis, where the cartilage breaks down and causes pain and stiffness in the joints.
Q2. Can you prevent damage to articular cartilage?
While some factors affecting articular cartilage health are beyond our control, such as genetics or aging, there are steps you can take to protect your joint health. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and avoiding excessive impact on your joints can all help preserve the integrity of your articular cartilage.
Q3. Is surgery always necessary for repairing damaged articular cartilage?
Not necessarily! Depending on the extent of damage and individual circumstances, non-surgical treatments like physical therapy, medication, or injections may be sufficient for managing symptoms and promoting healing.
Q4. Are there any supplements that support articular cartilage health?
Some studies suggest that supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate may have potential benefits for joint health by supporting the structure of articular cartilage. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Remember: taking care of your joints is crucial for maintaining overall mobility and quality of life. Stay informed about how to keep your articular cartilage healthy so you can continue moving comfortably for years to come!