Introduction to Anatomical Position
Welcome to the fascinating world of anatomical position! Have you ever wondered how healthcare professionals, researchers, and even artists navigate the complex landscape of the human body? Understanding anatomical position is like having a secret map that unlocks the mysteries of our anatomy. Join us on this journey as we delve into the key characteristics, historical context, and clinical relevance of anatomical position. Whether you’re a medical student eager to learn or simply curious about what makes us tick, this article has something for everyone. Let’s dive in!
Historical Context
In understanding anatomical position, delving into its historical context provides valuable insights. Dating back to ancient Greece, the renowned physician Hippocrates laid the foundation for anatomical studies by emphasizing observation and documentation. Fast forward to the Renaissance period, where scholars like Leonardo da Vinci revolutionized anatomical illustrations with unparalleled precision.
During the 19th century, figures such as Andreas Vesalius made significant contributions to human anatomy through detailed dissections and publications. The development of modern medical education in the 20th century further solidified the importance of anatomical knowledge in healthcare practices.
Exploring the historical evolution of anatomical position not only showcases human curiosity and innovation but also highlights the continuous quest for understanding our bodies’ intricacies across centuries.
Key Characteristics of Anatomical Position
When discussing the key characteristics of anatomical position, it’s essential to understand that this standard reference point in anatomy serves as the basis for describing the structures and relationships within the human body.
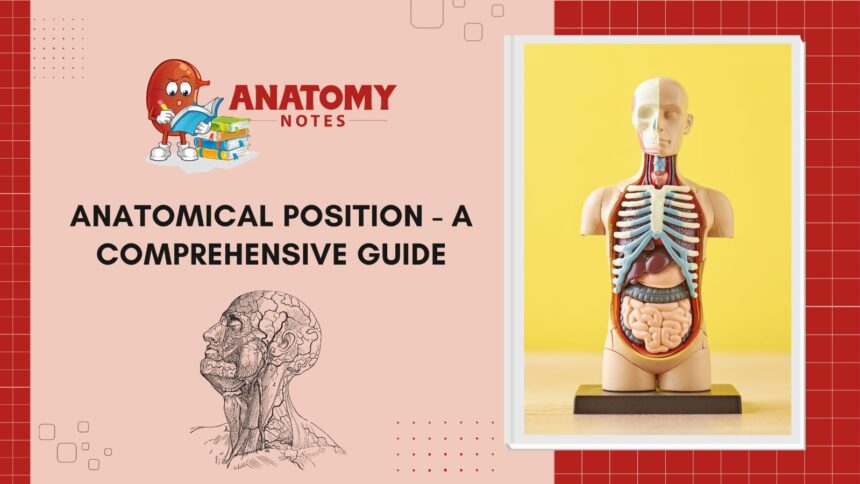
One significant aspect is that anatomical position assumes the body standing upright, facing forward with arms at the sides, palms facing forward, and feet parallel. This standardized stance allows for consistent communication among healthcare professionals and researchers.
Moreover, anatomical position provides a frame of reference for defining directional terms such as superior (above), inferior (below), anterior (front), posterior (back), medial (towards the midline), and lateral (away from the midline).
Additionally, maintaining consistency in using anatomical position aids in accurate medical diagnoses, surgical procedures, and understanding how different parts of the body interact spatially.
Understanding these key characteristics not only facilitates clear communication within healthcare settings but also forms a fundamental pillar of studying human anatomy comprehensively.
Anatomical Planes and Sections
Anatomical planes and sections are essential concepts in understanding the three-dimensional structure of the human body. These imaginary flat surfaces help anatomists visualize and describe the relative position of body parts. The three primary planes are sagittal, frontal (coronal), and transverse (horizontal).
The sagittal plane divides the body into left and right halves, while the frontal plane divides it into front (anterior) and back (posterior) sections. The transverse plane separates the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) portions. By utilizing these planes, medical professionals can accurately communicate about specific locations within the body.
Additionally, anatomical sections refer to actual cuts or slices through these planes for detailed examination purposes. Different imaging techniques like CT scans or MRIs rely on these principles to provide clear visuals of internal structures for diagnostic purposes. Understanding anatomical planes and sections is crucial for medical students, healthcare professionals, and researchers alike.
Directional Terms in Anatomy
Understanding directional terms in anatomy is crucial for accurately describing the location of body parts. Terms like superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, proximal, and distal help provide precise information about where structures are located in relation to each other.
For example, when discussing the positioning of organs or bones within the body, using directional terms ensures clear communication among healthcare professionals. Imagine trying to explain a surgical procedure without being able to accurately describe the exact location of an incision or target area – it would be chaotic!
By mastering these directional terms, medical professionals can communicate effectively during procedures and diagnoses. They serve as a universal language that transcends barriers and allows for accurate understanding regardless of geographical or cultural differences.
So next time you hear phrases like “proximal phalanx” or “inferior vena cava,” remember that these directional terms play a vital role in anatomical precision and clarity.
Importance in Medical Imaging
Understanding anatomical position is crucial in the field of medical imaging. When conducting diagnostic tests like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans, healthcare professionals rely on a standardized reference point to accurately interpret images.
By knowing the body’s default positioning, radiologists and technicians can pinpoint abnormalities or injuries with precision. This knowledge helps them identify structures and organs correctly, leading to accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Medical imaging techniques allow for non-invasive visualization of internal structures, aiding in early detection of diseases or conditions that may not be visible from the outside. Anatomical position provides a universal language for describing locations within the body during image analysis.
In emergency situations where time is critical, having a solid grasp of anatomical position ensures swift and accurate assessments can be made based on imaging results. It ultimately plays a vital role in providing quality patient care and improving health outcomes through effective medical interventions.
Comparative Anatomy
In the realm of anatomy, comparative anatomy plays a crucial role in understanding the similarities and differences across various species. By examining the anatomical structures of different organisms, scientists can uncover evolutionary relationships and adaptations that have occurred over millions of years.
Comparative anatomy allows researchers to draw parallels between species, shedding light on shared ancestry and divergent evolutionary paths. By comparing skeletal structures, organs, and physiological processes, scientists can piece together the puzzle of how life forms have evolved and adapted to their environments.
This field not only provides insights into the diversity of life on Earth but also offers valuable perspectives for medical research. By studying anatomical variations among species, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of human biology and potential implications for health and disease.
Comparative anatomy serves as a window into the wonders of evolution and biological diversity, offering endless opportunities for exploration and discovery in the world of science.
Common Misconceptions
Let’s address some common misconceptions surrounding anatomical position. One prevalent misunderstanding is that anatomical position varies from person to person, when in fact it remains consistent across individuals. Another misconception is that anatomical position only applies to humans, but this reference point is universal in the study of anatomy for all species.
Furthermore, some may believe that understanding anatomical position is only relevant for medical professionals or students pursuing a healthcare career. However, grasping this fundamental concept can benefit anyone interested in learning more about their own body and how it functions.
It’s also important to dispel the myth that memorizing directional terms and planes in anatomy is tedious and unnecessary. On the contrary, these concepts provide a precise language for describing the location and orientation of structures within the body.
By debunking these misconceptions, we can appreciate the significance of anatomical position as a foundational aspect of studying anatomy and physiology.
Clinical Relevance
Understanding the anatomical position is crucial in various clinical settings. When healthcare professionals communicate about specific areas of the body, they rely on standardized terms and reference points to ensure accuracy and precision in diagnosis and treatment.
For instance, when a doctor describes a patient’s symptoms or locates an injury, using directional terms based on the anatomical position helps avoid confusion and ensures clear communication among medical teams.
In surgical procedures, precise knowledge of anatomical positioning is essential for successful outcomes. Surgeons must have a deep understanding of how structures are positioned relative to each other to navigate delicate tissues accurately.
Medical imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs heavily depend on the anatomical position for interpretation. Radiologists use this standard frame of reference to analyze images accurately and identify abnormalities or pathologies within the body.
Moreover, medical students learning anatomy need a solid grasp of the anatomical position to comprehend complex relationships between organs, muscles, bones, and nerves. This foundational knowledge forms the basis for their future clinical practice.
Teaching Anatomical Position
Teaching anatomical position is crucial in the field of anatomy and medicine. It serves as the foundation for understanding the human body’s structure and function. Instructors use various methods such as diagrams, models, and interactive activities to engage students in learning this fundamental concept.
By emphasizing hands-on learning experiences, educators can help students grasp the spatial relationships of different body parts accurately. This approach helps students apply their knowledge effectively in clinical settings later on.
Through repetition and practice, learners can develop a solid understanding of anatomical position. By encouraging active participation and critical thinking, instructors enhance students’ retention and comprehension of this essential concept.
Teaching anatomical position plays a vital role in shaping future healthcare professionals’ skills and abilities to diagnose and treat patients effectively.
Practical Exercises
Ready to put your knowledge of anatomical position to the test? Practical exercises are a great way to solidify your understanding and improve retention.
One effective exercise is labeling diagrams of the human body in anatomical position. This hands-on approach helps reinforce key structures and their relative positions.
Another fun activity is practicing directional terms with a partner. By giving and following instructions using terms like superior, inferior, medial, lateral, proximal, and distal, you can enhance your grasp of anatomy.
For a more visual approach, try creating 3D models or sculptures depicting anatomical structures in their proper orientation. This tactile experience can deepen your appreciation for the complexity of the human body.
Remember, practice makes perfect when it comes to mastering anatomical position! So don’t hesitate to get creative with your exercises and keep challenging yourself.
Conclusion and Recap
As we come to the end of this journey through the anatomical position, it’s important to reflect on all that we’ve uncovered. From its historical roots to its practical applications in medical imaging and beyond, the anatomical position serves as a foundational concept in the field of anatomy.
By understanding the key characteristics, directional terms, and anatomical planes associated with this position, we gain valuable insight into how our bodies are structured and connected. This knowledge is not only crucial for healthcare professionals but also for anyone looking to deepen their understanding of human anatomy.
Whether you’re a student learning about comparative anatomy or a clinician applying these principles in a clinical setting, mastering the anatomical position opens up a world of possibilities. So next time you encounter this term in your studies or work, remember its significance and relevance in shaping our understanding of the human body.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Still have some lingering questions about anatomical position? Here are a few common queries answered to provide you with more clarity:
Q1. Why is it important to understand anatomical position?
Understanding anatomical position serves as the foundation for communication in the field of anatomy and medicine. It provides a standard reference point for describing the human body’s structures accurately.
Q2. How can I use anatomical position in daily life?
While not everyone needs to use anatomical terms in their everyday conversations, having a basic grasp of directional terms can help improve your understanding of medical information or discussions involving body movements.
Q3. Are there any practical exercises I can do to familiarize myself with anatomical position?
Yes! You can try labeling diagrams, practicing directional terms during workouts, or even using interactive anatomy apps to reinforce your knowledge of anatomical positions.
By delving into these frequently asked questions, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the intricate world of human anatomy through the lens of its fundamental reference point – anatomical position.