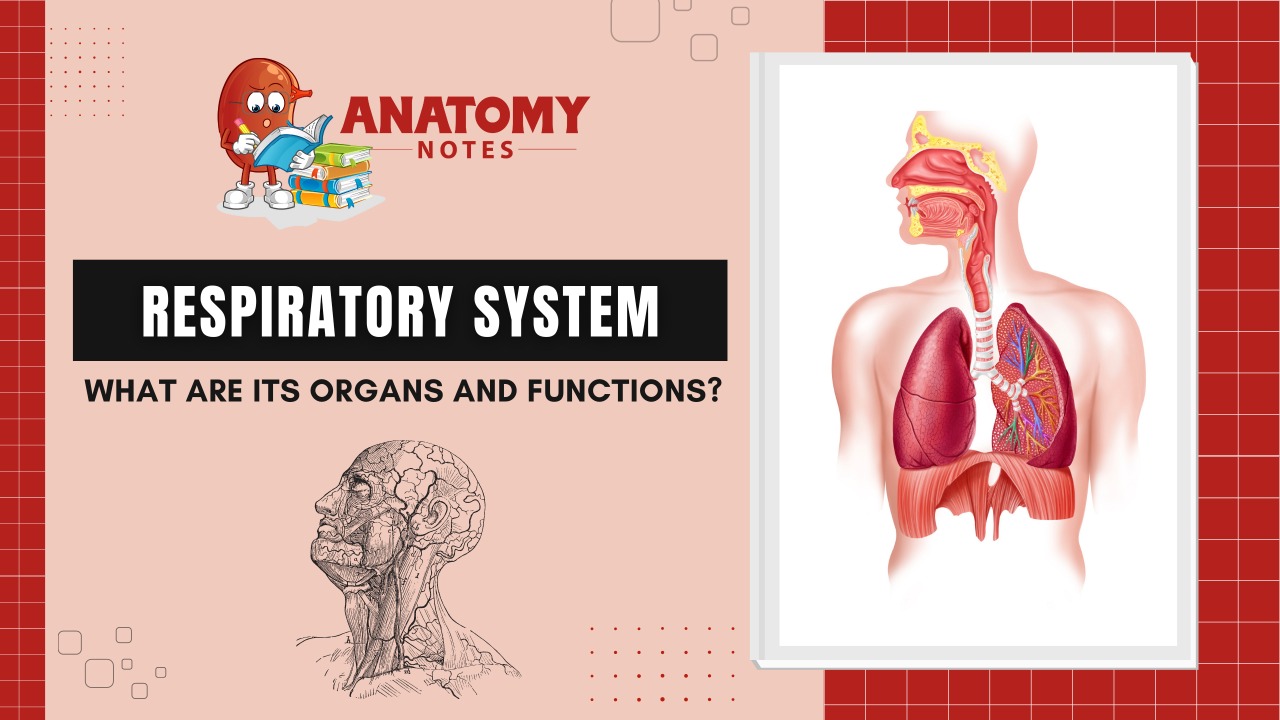
The respiratory system provides the route by which the supply of oxygen present in the atmospheric air, gain entry to the body and it provides the route of excretion of co².
The cells of the body need energy for there chemical activity that maintains homeostasis.
Most of this energy is derived from take place in the presence of oxygen. The main waste product of these reaction is carbon dioxide.
The condition of atmospheric air entering the body varies considerably according to the external environment as the air moves in, through the air passage to reach the lungs, it is warmed as cooled to the body temperature, moisture to become saturated with water vapours.
Blood provides the transport system for these gases between the lungs and the cells of the body.
Exchange of gases between the blood and the lungs is called external respiration, the exchange of gases between the blood and cells is called internal respiration.
The respiratory system consists of the following major components:
- Two lungs, the vital organs of the respiratory system
- Upper and lower airways that conduct, or move, gas into and out of the system
- Terminal air sacs called alveoli surrounded by a network of capillaries that provide for gas exchange
- A thoracic cage that houses, protects, and facilitates the function of the system
- Muscles of breathing that include the main muscle, the diaphragm, and accessory muscles.
The respiratory system is responsible for providing all the body’s oxygen needs and removing carbon dioxide. In fact the body’s oxygen reserve lasts only about 4–6 minutes.
If that reserve is used up and additional oxygen is unavailable then death is the obvious outcome. Therefore, the body must continually replenish its oxygen by bringing in the oxygen molecules from the atmosphere.
In a general sense, the respiratory system is a series of branching tubes called bronchi and bronchioles that transport the atmospheric gas deep within our lungs to the small air sacs called alveoli, which represent the terminal end of the respiratory system.
To better visualize this system, look at a stalk of broccoli held upside down. The stalk and its branches represent the airways, and the green bumpy stuff on the end is like the terminal alveoli.
Also Read: Muscular system – Types of muscles, characteristics & functions
Muscular system – Types of muscles, characteristics & functions
Each alveolus is surrounded by a network of small blood vessels called capillaries.
This combination of the alveolar wall and the capillary wall is called the alveolar–capillary membrane and represents the connection, or for you computer buffs, the interface, between the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
This is where the vital process of gas exchange takes place and therefore it is also referred to as the respiratory membrane.
Before getting deeper into this process, let’s trace the journey that oxygen molecules must take to arrive at the alveolar–capillary membrane.
THE UPPER RESPIRATORY System
The upper airway is responsible for initially conditioning the inhaled air. It consists of the following :-
- the nose,
- mouth,
- pharynx,
- and larynx
They performs several other important functions. The upper airway begins at the two openings of the nose, called nares, or nostrils, and ends at the vocal cords.
The functions of the upper airways include:
- Heating or cooling inspired (inhaled) gases to body temperature (98.6°F [37°C] .
- Filtering particles from the inspired gases.
- Humidifying inspired gases to a relative humidity of 100%
- Providing for the sense of smell, or olfaction
- Producing sounds, or phonation
- Ventilating, or conducting, the gas down to the lower airways
THE LOWER RESPIRATORY System
- The airway network that leads to the lungs and then branches out into the various lung segments resembles an upside down tree and is sometimes called the tracheobronchial tree.
Functions of Respiratory system :-
- Gas exchange between the blood and external environment.
- Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place within the lungs in bronchioles.
- Purify ,humidify and warm the incoming air.
- Produce sound for communication.
Learn More: