Both orthodontics and orthopedics repair musculoskeletal issues, particularly those involving the teeth, jaws, and face. Their titles and focus on health and beauty are similar, but they treat different challenges and use different approaches. To improve occlusion, function, and beauty, orthodontics aligns and positions teeth and jaws. Misaligned, overbites, underbites, and crowded teeth are corrected in this specialty. Orthodontists progressively shift teeth using braces, aligners, and retainers. By correcting dental and occlusal abnormalities, orthodontics can improve oral function and self-esteem.
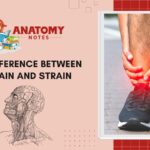
Alternatively, orthopedics treats musculoskeletal diseases and abnormalities. Orthopedics treats bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons, not only the mouth. Fractures, joint abnormalities, spinal deformities, and soft tissue injuries are treated by orthopedics. To restore mobility, relieve pain, and enhance musculoskeletal function, orthopedic doctors may prescribe surgery, physical therapy, medicines, or assistive devices.
The two disciplines differ most in their scope of practice. Orthodontics treats tooth and jaw alignment, whereas orthopedics treats musculoskeletal issues across the body. Orthodontic treatments are usually non-invasive and involve dental equipment, whereas orthopedic therapies can range from conservative to major surgery.
Orthodontics and orthopedics, two medical specialties, focus on various musculoskeletal issues. Orthodontics straightens teeth and jaws to improve dental appearance and function, whereas orthopedics treats musculoskeletal disorders. For proper dental, jaw, and musculoskeletal care, these variances must be understood. Patients obtain the most effective and suitable therapies by consulting with orthodontists for oral disorders and orthopedic surgeons for musculoskeletal issues.
Here are 44 differences between orthodontics and orthopaedics in a table format:
|
S.No. |
Aspects |
Orthodontics |
Orthopedics |
|
1 |
Medical Specialty |
Dental specialty that focuses on the alignment, position, and health of teeth and jaws |
Medical specialty that deals with the musculoskeletal system, including bones, joints, and muscles |
|
2 |
Area of Focus |
Primarily concerned with the correction of misaligned teeth and jaws |
Primarily concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal conditions and injuries |
|
3 |
Patients |
Typically treats patients with dental and orthodontic issues |
Typically treats patients with bone, joint, and muscle problems |
|
4 |
Practitioner |
Orthodontist |
Orthopedic surgeon, physician, or specialist |
|
5 |
Common Conditions |
Malocclusion (misalignment of teeth), overcrowding, overbites, underbites |
Fractures, arthritis, sports injuries, scoliosis, joint disorders |
|
6 |
Treatment Devices |
Uses braces, retainers, and other dental appliances |
May use casts, splints, braces, surgical interventions, and physical therapy |
|
7 |
Age of Patients |
Treats patients of all ages, including children and adults |
Treats patients of all ages, including children and adults |
|
8 |
Duration of Treatment |
Treatment duration varies but often lasts for months to several years |
Treatment duration varies depending on the condition and can range from weeks to lifelong management |
|
9 |
Primary Goals |
Improve dental aesthetics and functionality |
Relieve pain, improve function, and restore mobility of the musculoskeletal system |
|
10 |
Common Procedures |
Braces installation, teeth extractions, orthognathic surgery |
Joint replacement, fracture repair, tendon repair, spinal surgery |
|
11 |
Dental Health Focus |
Focuses on oral health, bite alignment, and facial aesthetics |
Primarily concerned with musculoskeletal health and functionality |
|
12 |
Diagnostic Tools |
X-rays, digital scans, bite impressions |
X-rays, MRI, CT scans, physical examinations |
|
13 |
Specialization |
Subspecialties like pediatric orthodontics, surgical orthodontics |
Subspecialties like sports medicine, pediatric orthopedics |
|
14 |
Education and Training |
Requires dental school, orthodontic residency |
Requires medical school, orthopedic residency |
|
15 |
Common Complaints |
Crooked teeth, gaps, difficulty chewing, speech problems |
Joint pain, fractures, muscle strains, mobility issues |
|
16 |
Collaborative Care |
Often collaborates with general dentists and oral surgeons |
Collaborates with physical therapists, rheumatologists, and other specialists |
|
17 |
Age of Onset for Conditions |
Dental misalignments can develop at any age |
Musculoskeletal conditions can develop at any age |
|
18 |
Surgery |
May perform orthognathic (jaw) surgery in complex cases |
Commonly performs surgical procedures like joint replacement, fusion, and repair |
|
19 |
Non-Surgical Approaches |
Focuses on non-surgical alignment whenever possible |
May use non-surgical treatments like physical therapy, medications, and rest |
|
20 |
Insurance Coverage |
Often covered by dental insurance plans |
Covered by various medical insurance plans |
|
21 |
Post-Treatment Care |
Requires retention (e.g., retainers) to maintain alignment |
May require ongoing monitoring and rehabilitation for some conditions |
|
22 |
Goals in Children vs. Adults |
In children, early intervention for proper dental development |
In adults, focus on addressing existing orthodontic issues |
|
23 |
Pain Management |
Generally, minimal pain or discomfort during treatment |
May involve pain management for injuries and post-surgical care |
|
24 |
Common Injuries Treated |
N/A |
Fractures, dislocations, sprains, and strains |
|
25 |
Genetic Factors |
Genetics can play a role in dental misalignments |
Genetics can contribute to musculoskeletal conditions |
|
26 |
Rehabilitation Focus |
Primarily focuses on dental rehabilitation |
Primarily focuses on musculoskeletal rehabilitation |
|
27 |
Importance of Routine Check-ups |
Emphasizes routine dental check-ups for maintenance |
May emphasize routine musculoskeletal health assessments |
|
28 |
Surgical Intervention Age Range |
Typically for older teenagers and adults |
Varies depending on the specific condition |
|
29 |
Cleft Lip and Palate Treatment |
Often involved in the treatment of cleft lip and palate |
Not typically involved in cleft lip and palate treatment |
|
30 |
Common Appliances |
Brackets, wires, bands, and aligners |
Crutches, braces, joint immobilizers, orthotics |
|
31 |
Cosmetic Considerations |
Emphasizes cosmetic dental improvements |
Primarily focuses on functional improvements |
|
32 |
Bracing Duration |
Braces are typically worn for a set period and then removed |
Bracing duration may vary significantly depending on the condition |
|
33 |
Physical Therapy Involvement |
Rarely involves physical therapy |
Often involves physical therapy for rehabilitation |
|
34 |
Impact on Speech |
May temporarily affect speech during adjustment |
May affect speech due to musculoskeletal conditions or surgeries |
|
35 |
Research Focus |
Dental and orthodontic research |
Musculoskeletal research and orthopedic advancements |
|
36 |
Long-Term Care |
May require occasional follow-up appointments for dental health |
May require lifelong management for certain musculoskeletal conditions |
|
37 |
Emergency Care |
Typically not involved in emergency musculoskeletal care |
Often involved in emergency fracture and dislocation care |
|
38 |
Treatment Emphasis in Elderly |
Focuses on orthodontic problems in the elderly, if necessary |
Addresses orthopedic issues more commonly in the elderly |
|
39 |
Intervention Timing |
Early intervention is common in children to guide dental development |
Timing of orthopedic intervention depends on the specific condition and age |
|
40 |
Genetic Testing |
May involve genetic testing for certain dental conditions |
May involve genetic testing for musculoskeletal disorders |
|
41 |
Airway Considerations |
May consider airway issues in relation to orthodontic treatment |
May consider airway issues in relation to musculoskeletal conditions |
|
42 |
Treatment Coordination |
Coordinates with other dental specialists as needed |
Coordinates with various medical specialists for comprehensive care |
|
43 |
Management of Chronic Conditions |
Typically does not manage chronic musculoskeletal conditions |
Manages chronic musculoskeletal conditions through medical and surgical approaches |
|
44 |
Role in Trauma Care |
Rarely involved in trauma care |
Often involved in the care of musculoskeletal trauma and injuries |
Also read: 45 Difference Between Kinesiologist and Physiotherapist
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s):
Q1. What distinguishes orthodontics from orthopedics in dentistry?
Orthodontics aligns teeth and jaws to enhance dental health and appearance. It aligns teeth with braces, aligners, and other devices. In dentistry, orthopedic dentofacial therapies target skeletal imbalances and discrepancies in the face and jaw to assist growth and alignment.
Q2. What benefits do orthodontic treatments provide beyond aesthetics?
Orthodontic treatments enhance smile beauty and function. Reducing cavities, gum disease, and irregular wear by aligning teeth and bites improves oral health. Alignment also improves eating and speaking.
Q3. Can orthopedics treat regions other than the face and jaw?
Orthopedics treats musculoskeletal problems worldwide. Orthopedic dentofacial dentistry treats jaw and facial structures. Orthopedics addresses disorders with bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and joints in numerous body areas.
Q4. What age is best for orthodontics?
All ages can benefit from orthodontic treatment. Teenagers get therapy since most permanent teeth have erupted. Adults also benefit from orthodontics. Some instances require early intervention in children to guide jaw development.
Q5. Are there orthodontic therapies other than braces?
Traditional braces have alternatives. Clear aligners like Invisalign are becoming popular. These translucent, detachable trays rearrange teeth gradually. Other options include lingual braces, which are affixed to the back of teeth and less apparent. Your orthodontist can recommend the best treatment for your requirements and preferences.